The Rotary disk filter is a widely used solid-liquid separation device. Its advantage lies in combining the separation capability of vacuum adsorption with the continuous operation characteristics of a disc-type structure, effectively achieving low-energy consumption and high-throughput solid-liquid separation operations.
Rotary disk filter:
The Rotary disk filter is designed around the core principles of “high-efficiency separation + stable operation.” Its key components and functions are as follows:
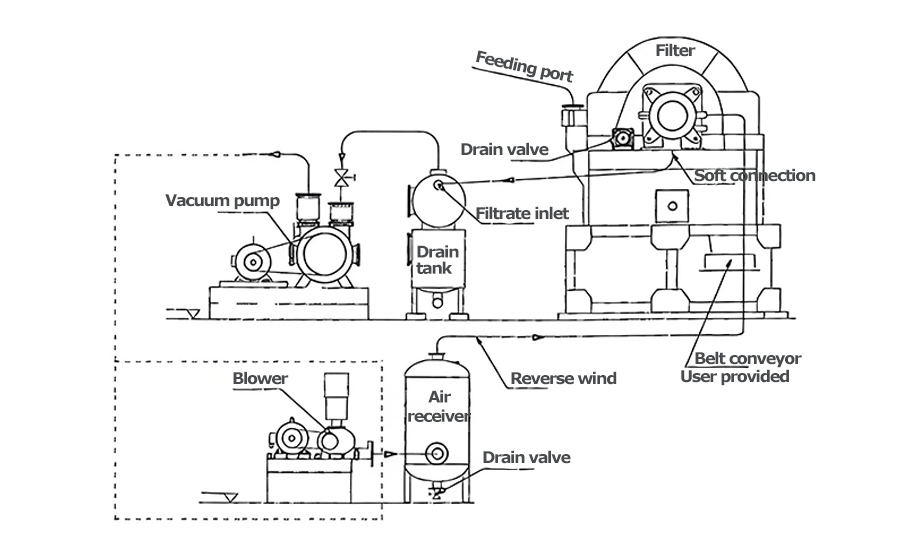
Main Frame: Includes a circular filter tank (for slurry loading, material selected based on corrosion resistance: 304/316L stainless steel, fiberglass reinforced plastic, or rubber-lined), the core rotary disc assembly, and a gear motor drive unit.
Rotary Disc Assembly: The equipment's core, composed of 8-24 segmented filter discs (quantity determined by processing capacity). Each disc features a honeycomb/lattice-style liquid collection chamber internally, covered externally with filter cloth.
Vacuum and Backwash System: Includes a vacuum pump, vacuum piping, compressed air storage tank, and backwash piping. Pipes connect to the disc assembly via rotating joints to ensure sealing, enabling vacuum adsorption and backwash sludge discharge respectively.
Washing System: Comprising a washing liquid tank, spray pump, spray pipes, and nozzles. Nozzles feature adjustable angles and flow rates (0.5–5 m³/h, matched to slurry throughput) to ensure uniform washing liquid coverage of the filter cake.
Discharge and Conveying System: Includes stainless steel/wear-resistant alloy scrapers (0.1–0.3 mm gap from filter cloth), optional vibration devices, and downstream conveying equipment. Scrapers remove filter cake, which is promptly transported away by conveying equipment to prevent accumulation.
Control System: Primarily PLC-based, providing real-time monitoring of rotational speed, vacuum level, liquid level, and wash liquid flow rate. Supports touchscreen parameter configuration and fault alarms (e.g., filter cloth blockage, vacuum pump failure). High-end models can integrate with plant DCS systems for full automation.
Equipment selection prioritizes “filtration area” as the key metric, commonly ranging from 5 to 100 m², with custom solutions exceeding 200 m². Slurry processing capacity spans 1 to 50 m³/h, determined by slurry solids content and particle size.
Core Advantages:
Compared to traditional solid-liquid separation equipment such as plate-and-frame filter presses, chamber filter presses, and centrifugal filters, Rotary disk filter offer the following significant advantages:
1. Continuous Operation with High Efficiency: Utilizing a rotating disc design eliminates the intermittent “plate loading-filtering-resting” cycle required by plate-and-frame machines, enabling 24/7 continuous operation. It achieves higher throughput per unit filtration area, making it ideal for large-scale applications like chemical wastewater treatment and mineral processing.
2. High Automation: PLC-based systems enable fully automated processes, reducing labor costs. Filter cloth replacement is straightforward, resulting in significantly lower maintenance burdens compared to traditional equipment.
3. Low Filter Cake Moisture Content: The “pre-dewatering + deep dewatering + reverse-blow” process achieves filter cake moisture content 10%-20% lower than centrifuges and 5%-15% lower than conventional vacuum filters. For chemical sludge, every 10% reduction in moisture content saves 15%-20% in drying energy consumption.
4. Wide adaptability: Processes suspensions from 0.1 to 1000 μm. Stable separation achievable for low-viscosity (power plant desulfurization gypsum), high-viscosity (starch slurry), and corrosive materials (electroplating wastewater) through parameter adjustment, with minimal filter cloth clogging.
5. Stable, Safe, and Eco-Friendly: Rotation speed<5 rpm with minimal vibration and noise <85 dB. No high-speed rotating components ensure high safety. Closed/semi-closed filter tanks prevent slurry volatilization and odor dispersion, enabling sealed processing of toxic/hazardous materials.
Product image
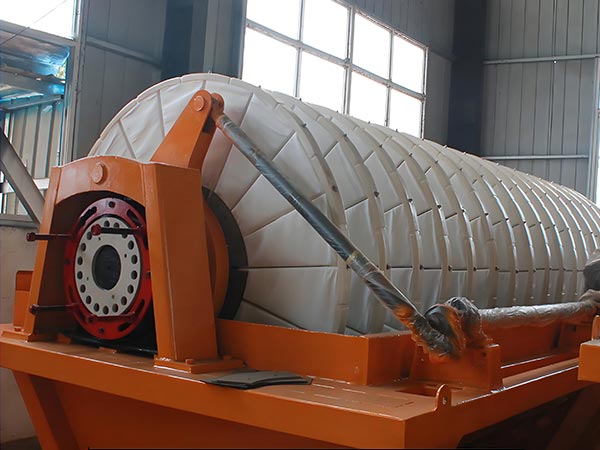
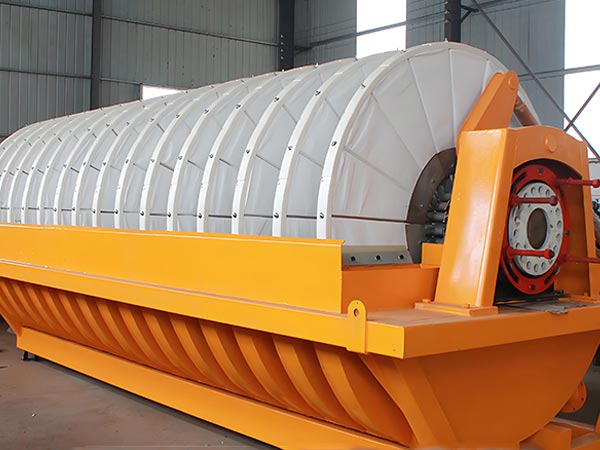
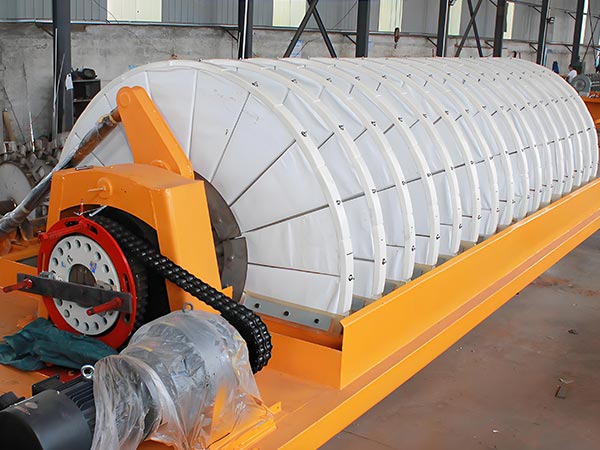
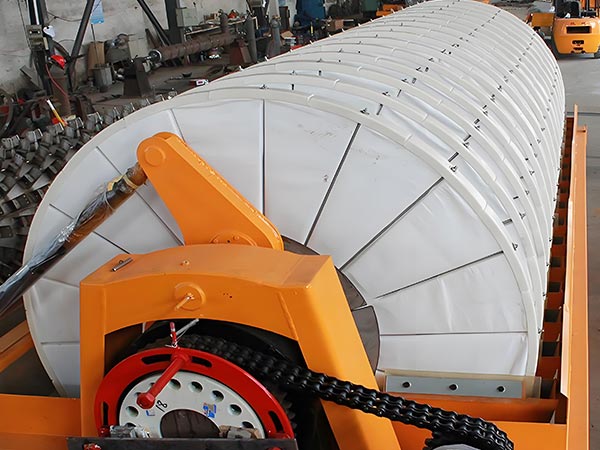




Technical Specifications of Rotary disk vacuum filter
Parameter name | Parameter range | Instructions |
filtration area | 0.5-200 ㎡ | 10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45、50、60、72、84、96、108、120㎡, etc |
Diameter of filter disc | 120-3100mm | Such as a large plate diameter of 2400 millimeters, a small plate diameter of 1200 millimeters, or 2100 millimeters, 3100 millimeters, etc |
Number of filter discs | 2-12 pieces | Depending on the filtering area, for example, when the filtering area is 10 square meters, the number of filter discs is 2, when it is 15 square meters, it is 3, and so on |
Number of filter fans per plate | 20 of them | Conventional configuration can strengthen the control of the filtration process, making the cake thickness uniform |
Filtration accuracy | 2-100 microns | Filter with different precision depending on the filter medium used, such as cellular cotton, filter cloth, filter paper, etc |
Filter pressure | 0.1-1.0 megapascal | Adjustable according to different models and application requirements |
Degree of vacuum | Not less than 91.2KPa | Approximately 684 millimeters of mercury to ensure filtration efficiency |
Processing power | 0.6-1.2 tons of dry ore per hour per square meter | The specific processing capacity is related to factors such as material properties, filtration area, etc |
Moisture content of filter cake | General materials not exceeding 26% | The moisture content of filter cake varies among different materials, and it can usually be controlled between 12% and 18% when processing phosphate concentrate |
Slurry concentration | 10%-65% | The optimal concentration of metal mineral slurry is 35% -65%, and the optimal concentration of coal or other light material slurry is 20% -40% |
Particle size of slurry | -100 mesh to -400 mesh | Suitable for slurry filtration within this particle size range |
Motor power | 2.2-15 kW | Including the power of the spindle motor and the mixing motor, for example, when the filtering area is 10 square meters, the power of the spindle motor is 2.2 kW and the power of the mixing motor is 3 kW; when the filtering area is 120 square meters, the power of the spindle motor is 11 kW and the power of the mixing motor is 15 kW |
Equipment material | Stainless steel, carbon steel, carbon steel liner, high molecular weight polyethylene, etc | Select different materials based on factors such as material corrosiveness |
Control system | PLC Control | Parameters such as filtering time, pressure, and cleaning of filtering media can be set as needed |
Application Scenarios:
Leveraging its highly efficient, continuous operation and strong adaptability, the rotary vacuum disk filter finds extensive application across multiple sectors including environmental protection, chemical processing, food manufacturing, and mining. Specific applications include:
1. Environmental Protection Industry:
Municipal wastewater treatment: Processes activated sludge and surplus sludge, achieving a filter cake moisture content<60% after dewatering for convenient subsequent landfill or incineration;
Industrial wastewater treatment: Handling chromium-contaminated sludge and saline sludge from chemical, electroplating, and dyeing wastewater to reduce solid waste volume;
Flue gas desulfurization: Dewatering desulfurization gypsum slurry from power plants and steel mills to produce gypsum with moisture content<15%, suitable for building materials production.
2. Chemical Industry:
Fine chemicals: Separating suspensions in synthetic resin and pigment production to ensure product purity;
Fertilizer Production: Treat phosphogypsum slurry and salt sludge from ammonium phosphate and potassium chloride production to recover by-products (e.g., phosphogypsum for sulfuric acid production);
Organic Chemicals: Separate ethanol, acetone, and other solvent-solid mixtures to enable solvent recovery.
3. Food Industry
Starch Processing: Filtration of starch slurry to obtain wet starch with 35%–45% moisture content, preparing it for subsequent drying;
Sugar Industry: Treatment of sugar beet and sugarcane filtration mud to recover sugars; mud can be processed into feed;
Dairy Processing: Filtration of whey protein suspensions and whey from cheese production to enhance product recovery rates.
4. Mining and Metallurgy Industry
Mineral Processing: Dewatering copper, iron, and gold ore concentrates to produce 10%-20% moisture content concentrate powder for efficient transportation and smelting;
Non-metallic Mineral Processing: Treating limestone and kaolin slurries to remove impurities and enhance purity;
Metallurgical Waste Treatment: Dewatering steel slag and red mud to reduce volume while recovering valuable metals like iron.
5. New Energy Industry
Lithium Battery Materials: Separating lithium iron phosphate and ternary material slurries from NMP solvent to ensure particle size and purity;
Photovoltaic Materials: Filtering quartz sand slurry to remove impurities and enhance photovoltaic glass purity;
Energy Storage Materials: Eliminating impurities from vanadium flow battery electrolytes to guarantee electrolyte purity and battery performance.
Hot Tags:













