What is a Sludge dewatering vacuum belt filter?
A Sludge dewatering vacuum belt filter is a continuous solid-liquid separation device that utilizes vacuum suction combined with belt compression. It is primarily used to dewater high-moisture sludge into low-moisture sludge cakes, facilitating subsequent transportation, landfill disposal, or resource recovery. As a continuous dewatering system, it features high throughput and a high degree of automation, making it widely applied in the environmental protection industry.

Working Principle of Sludge dewatering vacuum belt filter
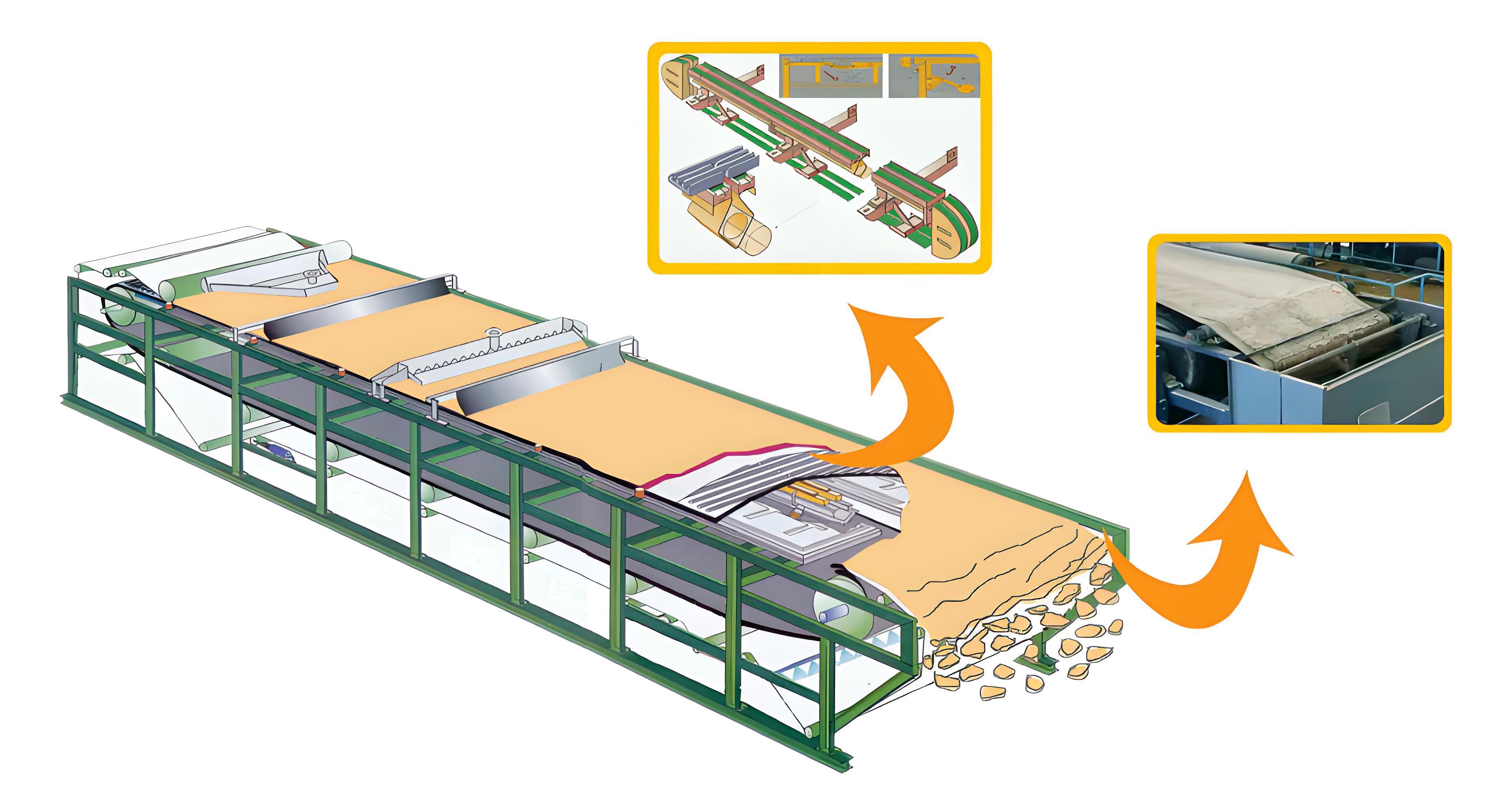
Sludge Distribution: Sludge is evenly distributed onto the filter belt by the feeding device;
Pre-dewatering Zone: Under gravity, sludge first sheds part of its free water;
Vacuum Dewatering Zone: The filter belt enters the vacuum chamber, where vacuum suction draws water from the sludge through the filter cloth, forming a drier sludge cake;
Pressurized Dewatering Zone: Some models feature press rollers to further squeeze the cake, reducing moisture content;
Discharge: At the belt's end, the cake is scraped off by a blade;
Filter Cloth Cleaning: An automatic cleaning system maintains the filter cloth for continuous reuse.
Advantages of Vacuum Belt filter presses for sludge dewatering
Continuous High-Efficiency Processing
Utilizing a continuous loop of filter belts enables 24/7 uninterrupted dewatering. With high throughput and efficiency, it is particularly suited for large-scale sludge treatment scenarios.
Superior Dewatering Performance
Combining vacuum adsorption with roller compression achieves deep dewatering. This significantly reduces cake moisture content and minimizes volume, facilitating subsequent transportation and disposal.
Low Energy Consumption
Primary energy use comes from vacuum pumps and drive systems, with overall energy consumption lower than traditional equipment like plate-and-frame filter presses. Reusable filter belts further reduce operating costs.
High Automation
Fully automates feeding, filtration, cleaning, and discharge processes. Equipped with web guiding and tensioning systems for stable operation and minimal maintenance.
Wide Applicability
Processes diverse sludge types including municipal sewage, chemical, metallurgical, and mining sludge. Demonstrates excellent adaptability to complex sludge characteristics such as high viscosity, fine particles, and oil content.
Reliable Operation
Features a compact, well-designed structure with low failure rates, enabling long-term stable operation. Suited for continuous, large-scale industrial environments.
Why Sludge Dewatering Matters
The importance of sludge dewatering is primarily reflected in the following aspects:
Volume Reduction: Undewatered sludge typically has a moisture content of 95%-99% and occupies a large volume. Dewatering reduces this to 75%-85%, shrinking the volume by 3-5 times and significantly lowering transportation, storage, and disposal costs.
Stabilization: Reduced moisture content minimizes odors, decay, and pathogens, making subsequent treatment safer.
Facilitates Subsequent Disposal: Whether for landfilling, incineration, composting, or construction material reuse, sludge must meet specific dryness requirements. Dewatering is a prerequisite for all subsequent disposal processes.
Reduces Environmental Risks: High-moisture sludge is prone to leakage and runoff, causing secondary pollution. Dewatering minimizes the risk of pollutant migration.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Sludge dewatering vacuum belt filter
During model selection, focus on the following key points that directly impact dewatering efficiency, operating costs, and equipment lifespan.
Sludge Properties
Includes sludge type, moisture content, viscosity, particle size, and presence of oil or chemicals. Different sludges impose vastly different demands on filter belts and vacuum levels.
Processing Capacity Requirements
Determine equipment width and operating speed based on daily wet sludge or dry solids throughput.
Dehydration Objectives
Define target final cake moisture content. Different processes demand varying vacuum levels, filter belt materials, and auxiliary chemicals.
Vacuum Level and Suction Capacity
Higher vacuum yields better dehydration but increases energy consumption. Select an appropriate vacuum system based on sludge characteristics.
Filter Belt Material and Lifespan
Common materials include polyester and polypropylene. Consider chemical resistance, tensile strength, air permeability, and cost.
Operational Stability
Includes web guiding system sensitivity, tensioning methods, and filter belt cleaning effectiveness, all directly impacting continuous equipment operation.
Energy Consumption and Maintenance Costs
Vacuum pumps account for the largest energy consumption share; compare energy consumption per unit of dry sludge. Also consider filter belt replacement cycles and wear part costs.
Automation Level
Features like automatic control, online monitoring, and remote diagnostics reduce labor costs and enhance stability.
Hot Tags:








